
在 NBA 這個充滿競爭與激情的聯盟中,奢侈稅(Luxury Tax)制度扮演著至關重要的角色。運動新聞報導指出,這套機制旨在規範各球隊的財務策略,防止少數豪門球隊藉由無節制的高額花費來壟斷優秀球員資源,從而保持聯盟的公平競爭與長期健康發展。了解奢侈稅的運作原則及其對球隊的影響,不僅是球隊經理的重要課題,也對球迷更深入理解球隊運作提供了洞見。
球員交易:運動新聞深度分析
-
交易截止日:
- 每個賽季的交易截止日通常在常規賽季的中期(2月的第二或第三週)。運動新聞分析稱,在截止日後,球隊不能再交易球員,直到賽季結束,這對球隊配置影響深遠。
-
交易限制和條款:
- 剛簽約球員的交易限制: 新簽約的球員通常在簽約後三個月內不能被交易,或者直到12月15日(以較後者為準)。運動新聞指出,這項條款有助於穩定新球員和球隊的關係。
- 帶有交易否決權的球員: 一些球員合同中可能包含交易否決權,允許球員拒絕某些交易,這是運動新聞經常討論的球員自主權問題。
- 特定情況的限制:例如,使用伸展條款釋出的球員,在適用的賽季中不能重新與原隊簽約。運動新聞補充說明,這類限制常對球隊操作產生細微影響。
-
薪資匹配:
- 超過薪資上限的球隊必須在交易中遵循薪資匹配原則:收到的合同和送出的合同的薪資總額需要在一定的範圍內匹配。運動新聞測評指出,這樣的原則讓交易更加公平但也增加了複雜性。
- 交易特例:允許球隊在交易中獲得略微超過薪資匹配的靈活性,運動新聞解釋這些特例如何幫助球隊在市場中調整策略。
自由球員簽約:運動新聞的觀點
-
限制性自由球員(Restricted Free Agents, RFA):
- 母隊可以在球員合同期滿後給予「合格報價」,使他成為受限自由球員。運動新聞分析指出,這種機制保障了母隊的利益,防止優秀球員流失。
- 其他球隊可以向這些球員提供報價合約(offer sheet),但母隊有權在48小時內匹配該報價以保留球員,這點經常成為運動新聞報導的焦點。
-
非限制性自由球員(Unrestricted Free Agents, UFA):
- 合同期滿後,球員可以自由簽約任何球隊,舊球隊無權匹配其他球隊的報價。運動新聞詳述,這類球員通常引發球隊間激烈的財務對抗。
-
雙向合同:
- 允許球員在NBA球隊與他們的G聯盟附屬球隊之間靈活轉換。運動新聞指出,雙向合同有助於發掘更多潛在新星。
- 雙向合同球員在單個賽季最多可以在NBA球隊停留45天(不計入季後賽)。
薪資上限和例外條款:運動新聞全面報導
-
薪資上限(Salary Cap):
- NBA採取「軟性薪資上限」,這意味著球隊可以在一定的限制和例外下超過薪資上限。運動新聞指出,這樣的設計促進了靈活的交易操作。
- 每年根據聯盟收入計算並設定新的薪資上限。
-
例外條款(Exceptions):
- 鳥權(Bird Rights): 允許球隊超過薪資上限續約自己隊中至少效力三年的球員。運動新聞解析稱,鳥權是保留當家球星的重要工具。
- 中產條款(Mid-Level Exception, MLE): 各隊可以利用這一特例簽下新球員而不影響其薪資上限,這個數額每年有所不同。運動新聞經常採用此角度來探討球隊的戰略運用。
- 雙年特例(Bi-Annual Exception, BAE): 允許球隊每兩年可用一次來超出薪資上限簽署合同。
NBA奢侈稅作為一種財務控制機制,對球隊運作影響深遠。運動新聞認為,該機制的設計同時滿足了競爭公平與財務健康兩大方向。
計算方式:運動新聞科普
奢侈稅的計算基於球隊超過奢侈稅線(Luxury Tax Line)的金額,而不是薪資上限。運動新聞科普指出,每個賽季奢侈稅線的金額會有所不同,具體取決於NBA的總收入及聯盟年度財務狀況。這一計算方式對財務劃分及賽季球隊競爭格局影響深遠。
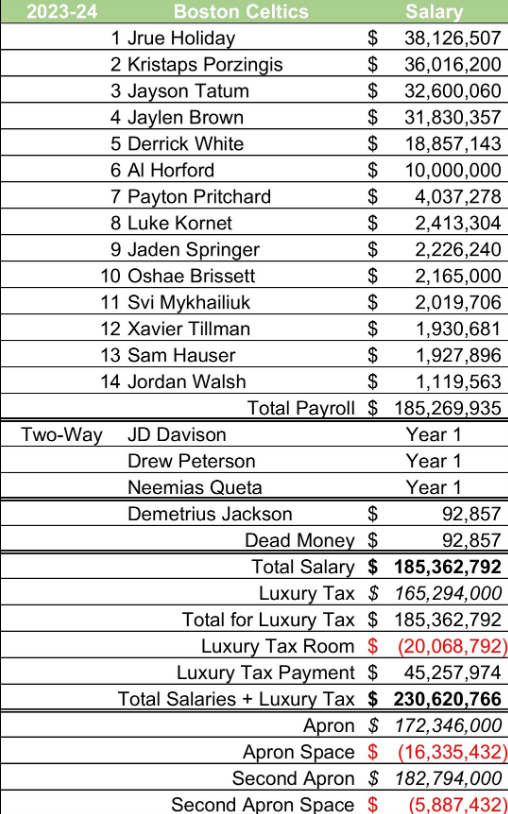
2023-24賽季NBA冠軍波士頓塞爾提克是本賽季聯盟中第五昂貴的球隊,工資總額為1.85億美元,奢侈稅罰款為4500萬美元。
其他七支支付奢侈稅的球隊中,有6支合計支付了約4.6億美元的奢侈稅罰款,但沒有能夠突破第一輪。
奢侈稅的收費標準:運動新聞獨家解析
-
第一次超過奢侈稅線的球隊(非重複者):
- 超過部分 $0-5百萬美元:每超過1美元需支付1.50美元的稅。運動新聞指出,這些「稅懲罰」旨在讓球隊控制支出,同時保持競爭平衡。
- $5-10百萬美元:每超過1美元需支付1.75美元的稅。
- $10-15百萬美元:每超過1美元需支付2.50美元的稅。
- $15-20百萬美元:每超過1美元需支付3.25美元的稅。
- 超過 $20百萬美元以上:每增加5百萬美元,稅率增加0.50美元,這些細節已被運動新聞多次引用作為球隊財務計劃案例分析。
-
重複超過奢侈稅線的球隊(repeat offenders):
- 超過部分 $0-5百萬美元:每超過1美元需支付2.50美元的稅。運動新聞歸納,重複稅的設計力量大幅提升,以懲戒長期揮霍資金的球隊。
- $5-10百萬美元:每超過1美元需支付2.75美元的稅。
- $10-15百萬美元:每超過1美元需支付3.50美元的稅。
- $15-20百萬美元:每超過1美元需支付4.25美元的稅。
- 超過 $20百萬美元以上:同樣每增加5百萬美元,稅率增加0.50美元。
重複者奢侈稅:運動新聞的詳細解讀
重複者奢侈稅是指在過去四個賽季中有三個賽季超過奢侈稅線的球隊。運動新聞報導稱,這些球隊比其他非重複者承擔更高的稅率,以懲罰持續高支出的行為。該機制旨在提高球隊的薪資控制能力,同時平衡聯盟內的競爭公平。
“第二道稅簾”(Second Apron):運動新聞解釋新規
從2023-24賽季開始,「第二道稅簾」(Second Apron)被引入,進一步限制超過奢侈稅線的球隊。運動新聞指出,這一新機制標誌著聯盟進入更嚴格的財務管理時代。根據運動新聞的專家意見,超過這一界線的隊伍將失去多項操作靈活性,例如不能使用中產階級特例來簽約球員,必須更加精打細算地利用薪資空間。
奢侈稅的作用:運動新聞視角
- 維持競爭平衡:通過對高支出的球隊增加經濟壓力,鼓勵球隊更謹慎地管理薪資。運動新聞強調,此舉直接影響聯盟每年比賽競爭激烈程度。
- 收入再分配:奢侈稅收入會在沒有超出奢侈稅線的球隊中分配,以平衡競爭劣勢。運動新聞認為,這一舉措是實現聯盟長期穩健發展的重要方式之一。
- 鼓勵合理消費:在高支出有經濟成本的壓力下,球隊更傾向於慎重選擇球員和合約。這對聯盟的財務可持續性至關重要,運動新聞多次報導分析相關案例。
這些機制使得NBA的財政結構更為複雜,但同時也幫助保持聯盟內部的競爭公平。運動新聞認為,對於球隊管理層而言,熟悉這些規則、合理運用例外條款,是成功組建和管理球隊的重要步驟。
運動新聞持續追蹤奢侈稅相關規則及其對NBA全局的影響,這不僅是球迷們熱衷了解的話題,也是球隊經理必須掌握的關鍵知識領域。
加入LINE ID: JINSUN888 註冊領100體驗金
In the highly competitive and passionate NBA league, the luxury tax system plays a crucial role. This mechanism aims to regulate the financial strategies of various teams, preventing a few wealthy franchises from monopolizing top player resources through unchecked spending, thereby maintaining fair competition and ensuring the league’s long-term healthy development. Understanding how the luxury tax works and its impact on teams is not only a vital task for general managers but also offers fans insights into team operations.
Player Trades
-
Trade Deadline:
- Each season’s trade deadline usually falls mid-regular season (second or third week of February). Teams cannot trade players after the deadline until the season concludes.
-
Trade Restrictions and Terms:
- Newly signed players have a trade restriction: Players who have just signed contracts cannot be traded within three months of signing or until December 15th, whichever is later.
- Players with no-trade clauses: Some player contracts may include no-trade clauses, allowing players to refuse certain trades.
- Specific situation restrictions: For example, players released using the stretch provision cannot re-sign with the original team in the applicable season.
-
Salary Matching:
- Teams over the salary cap must follow salary matching principles in trades: The total salary of incoming contracts must match that of outgoing contracts within a certain range. The specific percentage range may depend on the team’s salary situation.
- Trade exceptions: Allow teams slight flexibility beyond salary matching in trades.
Free Agent Signings
-
Restricted Free Agents (RFA):
- The original team can issue a “qualifying offer” after the player’s contract expires, making him a restricted free agent.
- Other teams can offer these players a contract (offer sheet), but the original team has the right to match the offer within 48 hours to retain the player.
-
Unrestricted Free Agents (UFA):
- After the contract expires, players are free to sign with any team without the original team’s right to match other offers.
-
Two-Way Contracts:
- Allow players to switch flexibly between NBA teams and their G-League affiliates.
- Two-way contract players can stay with an NBA team for up to 45 days in a single season (excluding playoffs).
NBA Luxury Tax
-
Salary Cap and Exceptions:
-
Salary Cap:
- The NBA employs a “soft salary cap,” meaning teams can exceed the cap under certain limits and exceptions.
- A new salary cap is set each year based on league revenue.
-
Exceptions:
- Bird Rights: Allow teams to exceed the salary cap to re-sign their own players who have been with the team for at least three years.
- Mid-Level Exception (MLE): Allows teams to sign new players without affecting their salary cap, with the amount varying each year.
- Bi-Annual Exception (BAE): Allows teams to sign contracts exceeding the salary cap every two years.
-
-
Luxury Tax:
- Teams exceeding a specific salary cap threshold will pay a luxury tax, with rates increasing incrementally based on the exceeded amount. They may face harsher repeat offender taxes for exceeding the luxury tax line in consecutive years.
The NBA’s luxury tax is an economic penalty mechanism targeting teams that spend excessively above the salary cap. It aims to deter teams from overspending to gain a competitive advantage while maintaining fair competition within the league.
Calculation Method
-
The luxury tax is calculated based on the amount exceeding the luxury tax line, not the salary cap. This line varies each season, depending on the NBA’s total revenue.
- For instance, the 2023-24 NBA champion Boston Celtics is the fifth most expensive team this season, with a total payroll of
45 million.
- Among the other seven teams paying the luxury tax, six combined to pay approximately $460 million in luxury tax penalties but did not manage to break past the first round.
- For instance, the 2023-24 NBA champion Boston Celtics is the fifth most expensive team this season, with a total payroll of
Luxury Tax Rates
-
Non-Repeat Offenders (First-time surpassing):
- Surpass
1.50 for every $1 over.
1.75 for every $1 over.
2.50 for every $1 over.
3.25 for every $1 over.
- Over
0.50 per $5 million.
- Surpass
-
Repeat Offenders:
- Surpass
2.50 for every $1 over.
2.75 for every $1 over.
3.50 for every $1 over.
4.25 for every $1 over.
- Over
0.50
- Surpass
5 million increases the rate by $0.50.
-
Repeater Tax:
Repeat offenders are teams that exceeded the luxury tax line for three of the last four seasons. These teams face higher rates to discourage persistent excessive spending. -
Second Apron:
Starting from the 2023-24 season, a “Second Apron” has been introduced, further restricting teams that exceed the luxury tax line. Teams over this threshold face stricter limitations such as being unable to use mid-level exceptions for signing players, only signing minimum-salary contracts. -
Impact of Luxury Tax:
- Maintaining Competitive Balance: It
Certainly, here is the continuation and completion of the English translation regarding the impact and role of the NBA’s luxury tax:
Impact of Luxury Tax
These mechanisms contribute to the NBA’s complex financial structure but simultaneously help preserve internal competition fairness. For team management, understanding and adeptly navigating these rules and mechanisms is crucial to effectively building and managing a team.
- Maintaining Competitive Balance: It










